
Created by - Elite Offshore
The Importance of Fire Fighting and Rescue Training for Everyone
Fire—it's a force of nature that has both the power to sustain life and the potential to destroy it. In our modern world, where fires can break out anywhere, from homes to workplaces, the importance of fire fighting and rescue training cannot be overstated. In this article, we'll understand the various types of fires, fire extinguishing mediums, safety precautions, and why fire training is essential for everyone's safety.Understanding the Nature of Fire:Before we explore the intricacies of fire fighting and rescue training, it's crucial to understand the nature of fire itself. Fire is the result of a chemical reaction known as combustion, which occurs when a fuel source combines with oxygen and heat. This reaction releases energy in the form of heat and light, sustaining the fire and allowing it to spread if not controlled.There are several types of fires, each classified based on the type of fuel involved. These classifications include:1. Class A Fires: These fires involve ordinary combustible materials such as wood, paper, cloth, and plastics. Class A fires are among the most common and can occur in homes, offices, and industrial settings.2. Class B Fires: Class B fires involve flammable liquids and gases such as gasoline, oil, propane, and solvents. These fires can be particularly dangerous due to the volatility of the fuel involved.3. Class C Fires: Class C fires involve energized electrical equipment, such as electrical panels, wiring, and appliances. Attempting to extinguish a Class C fire with water can pose a significant risk of electrocution.4. Class D Fires: Class D fires involve combustible metals, such as magnesium, titanium, and sodium. These fires are relatively rare but can occur in industrial settings where metal powders or shavings are present.5. Class K Fires: Class K fires involve cooking oils and fats, typically found in commercial kitchens and restaurants. These fires can be extremely hot and difficult to extinguish using traditional methods.Fire Extinguishing Mediums:Effective fire fighting requires the use of appropriate extinguishing mediums tailored to the type of fire involved. Here are some common fire extinguishing agents and their applications:1. Water: Water is the most commonly used extinguishing agent for Class A fires, as it cools the fuel and removes heat from the fire. However, water should not be used on Class B, C, or D fires, as it can spread flammable liquids, conduct electricity, or react violently with certain metals.2. Foam: Foam extinguishers are effective for Class A and B fires, as the foam creates a barrier between the fuel and the oxygen, smothering the fire. Foam extinguishers are commonly used in industrial settings and areas where flammable liquids are present.3. Carbon Dioxide (CO2): CO2 extinguishers are suitable for Class B and C fires, as the CO2 displaces oxygen, suffocating the fire. CO2 extinguishers are non-conductive and leave no residue, making them ideal for use on electrical equipment.4. Dry Chemical Powder: Dry chemical powder extinguishers are versatile and effective for Class A, B, and C fires. The powder interrupts the chemical reaction of the fire and forms a barrier that prevents reignition. However, care should be taken when using dry chemical powder near sensitive equipment or electronics, as the powder can be corrosive.5. Wet Chemical: Wet chemical extinguishers are specifically designed for Class K fires involving cooking oils and fats. The wet chemical forms a soapy layer on the surface of the fuel, preventing it from reigniting.Safety Precautions and Training:While fire extinguishers and other firefighting equipment are valuable tools for combating fires, proper training is essential to ensure their effective use. Fire fighting and rescue training provide individuals with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to respond quickly and safely in the event of a fire emergency.Training programs cover a wide range of topics, including:1. Fire Prevention: Understanding the causes of fires and implementing preventive measures to reduce the risk of fire incidents.2. Fire Detection and Alarm Systems: Recognizing the signs of a fire and responding promptly to activate alarm systems and alert others to evacuate.3. Evacuation Procedures: Knowing the designated evacuation routes, assembly points, and procedures for safely evacuating occupants from a building or area.4. Fire Extinguisher Use: Learning how to select the appropriate extinguishing agent for the type of fire, operate fire extinguishers correctly, and maintain safe distances from the fire.5. Emergency Communication: Effectively communicating with emergency responders, colleagues, and occupants during a fire emergency to coordinate evacuation and rescue efforts.6. First Aid and Rescue Techniques: Providing basic first aid to individuals injured during a fire emergency and performing rescue operations to evacuate trapped or injured occupants.Elite Offshore Pvt Ltd: A Commitment to Fire Fighting and Rescue TrainingAt Elite Offshore Pvt Ltd, we understand the critical importance of fire safety and rescue training in safeguarding lives and property. Through our comprehensive training programs, we equip individuals with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to respond effectively to fire incidents and emergencies.Our training modules cover a wide range of topics, including fire prevention, fire extinguisher usage, evacuation procedures, and first aid techniques. We utilize state-of-the-art facilities and experienced instructors to deliver hands-on training that simulates real-world scenarios, ensuring participants are well-prepared to handle emergencies with competence and composure.Moreover, our commitment to continuous improvement drives us to stay abreast of the latest developments in fire safety technology and best practices. We regularly update our training programs to incorporate industry advancements and regulatory changes, ensuring our participants receive the most relevant and up-to-date instruction.Through our unwavering dedication to excellence in fire fighting and rescue training, Elite Offshore Pvt Ltd is proud to contribute to the safety and well-being of individuals and communities across India. Together, let's prioritize fire safety education and preparedness to prevent disasters and protect what matters most—our lives. Get in touch with us on training@eliteoffshore.in.Fire fighting and rescue training should be accessible to everyone, regardless of their occupation or level of experience. Employers, educational institutions, community organizations, and government agencies play a vital role in providing and promoting fire safety training initiatives.Conclusion:Fire fighting and rescue training are essential components of fire safety preparedness for individuals and organizations alike. By understanding the nature of fire, the different types of fires, and the appropriate extinguishing agents, individuals can effectively respond to fire emergencies and minimize the risk of injury or property damage.Moreover, fire safety training instills a culture of awareness, responsibility, and preparedness, empowering individuals to take proactive measures to prevent fires and protect themselves and others. As the saying goes, "prevention is better than cure," and investing in fire safety training is an investment in the safety and well-being of our communities.Stay safe, stay prepared, and never underestimate the importance of fire fighting and rescue training.
More detailsPublished - Wed, 05 Jun 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Crane Operator: A rewarding and fulfilling career
A career as a crane operator can be quite lucrative and rewarding. However, this being a skill, depends on individual interest. Here are some factors to consider:1. Crane operators are often in demand, especially in offshore, construction, shipping, and manufacturing industries. As infrastructure projects increase and construction continues to expand globally, the need for skilled crane operators remains steady.2. Crane operators can earn a good income. Salaries vary based on factors such as location, experience, and type of crane operated, but generally, they can earn above-average wages.3. Operating a crane requires specialized skills and training. As you gain experience and expertise, you may have opportunities to operate more advanced equipment or move into supervisory roles. The training for offshore Offshore Crane Operators are in 3 stages. It takes time to become an Offshore Crane Operator Stage 3 operator. Elite Offshore Pvt Ltd, based in Navi Mumbai, provides training and certification of crane operators for Mobile RT Crane, Offshore Crane, EOT Crane, Hydra & Farana etc. They also provide training and certification for Crane Inspectors. You may get in touch with them for more details..4. As long as construction and related industries exist, crane operators will be needed. This provides a certain level of job stability, although economic fluctuations can affect demand to some extent.5. Crane operators often work outdoors and in various weather conditions. They may also work at heights, which can be challenging for some individuals but exciting for others. The offshore crane operators work on offshore rigs. There are floating cranes with capacity in thousands of tonnes.6. Operating heavy machinery like cranes comes with inherent risks. Safety protocols must be followed diligently to prevent accidents and injuries.Thus a career as a crane operator can be fulfilling for those who enjoy working with heavy machinery, have a good sense of spatial awareness, and are committed to safety. It offers a combination of job stability, good pay, and opportunities for advancement for those willing to invest in training and gaining experience.
More detailsPublished - Wed, 12 Jun 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Fire Extinguisher Checklist: Key components
Having a checklist for fire extinguisher checks is crucial to ensure that no item to check is missed out during the course of checking the extinguishers. The fire extinguishers should always be in ready condition for use when required. To ensure this, it is essential that each aspect of the extinguisher's functionality and readiness is thoroughly examined.Following are the key components of a checklist for monthly, annual, and periodical checks on a fire extinguisher. 1. Visual Inspection: - Check for any physical damage, such as dents, corrosion, or leaks. - Ensure the pressure gauge or indicator is in the proper range. - Verify that the safety pin and tamper seal are intact.2. Accessibility: - Confirm that the fire extinguisher is easily accessible and not obstructed by any objects. - Ensure that the extinguisher's location is clearly marked with appropriate signage.3. Operating Instructions: - Check that the operating instructions and labels are legible and facing outward. - Ensure that users understand how to operate the extinguisher.4. Pressure: - Verify that the pressure gauge is within the recommended range. - For pressurized extinguishers, check for any signs of leakage.5. Seals and Labels: - Confirm that all seals and labels are intact and not damaged. - Ensure that the inspection tag is up-to-date.6. Nozzle and Hose: - Inspect the nozzle and hose for any blockages, cracks, or other damage. - Ensure that the hose is securely attached to the extinguisher.7. Agent: - Check the agent for any signs of clumping or settling, which may affect discharge effectiveness. - Verify that the agent is appropriate for the types of fires it's intended to extinguish.8. Functionality: - Test the operation of the extinguisher (if allowed) by discharging a small amount of agent to ensure it functions correctly. - Ensure that the discharge lever or handle operates smoothly.9. Maintenance Records: - Review the extinguisher's maintenance records to ensure that all required inspections and servicing have been completed.10. Training: - Confirm that individuals responsible for using the extinguisher are adequately trained in its operation and maintenance.These key points may be included in the checklist. Depending on type of extinguisher and its manufacturer, inspections may be required on monthly, annual or periodical basis. Check manufacturer instructions. These checks are important to ensure that fire extinguishers are properly maintained and ready for use in case of emergency.This topic is adequately covered in detail during Advance Fire Fighting training conducted at Elite Offshore Pvt LtdFor further information, please contact training@eliteoffshore.in or call +91-22-4970 4933 or +91-80 9747 2277. You may visit our website Elite Offshore Pvt Ltd (for all courses) or Ecademy The E-Learning Academy (for e-learning courses).Visit our training centre at below address:Elite Offshore Pvt. Ltd.G- 5, Platform Level, Tower-3, Belapur Railway Station Complex, Sector-11, C.B.D. Belapur, Navi Mumbai-400614.Contact No. +91-80-9747-2277, +91-22-4970-4933, +91-22-4600-3839Email: info@eliteoffshore.in or training@eliteoffshore.in
More detailsPublished - Wed, 12 Jun 2024
Created by - Elite Offshore
Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S): Accidents and Prevention in construction industry
Hydrogen Sulphide Gas (H2S) accidents are not as common in the construction industry as in other sectors like oil and gas or wastewater treatment. However, they do occur and can be extremely dangerous when they happen. Hydrogen sulfide is normally formed where organic matter is decomposing under anaerobic (oxygen-free) conditions. It is a toxic and flammable gas.Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S) Accidents in Construction industry may be present in:1.Confined Space Entry (CSE): H₂S accidents in the construction industry often occur in confined spaces such as sewers, manholes, and underground utility vaults. Workers entering these spaces without proper atmospheric testing and ventilation are at risk of exposure.2.Excavation, Trenching and Shoring Sites: Construction sites involving excavation near areas with known contamination or organic matter (e.g., near landfills or wastewater treatment facilities) can pose a risk of H₂S exposure.3.Decomposition of Organic Material: Construction activities in areas with high concentrations of organic materials, such as certain types of soil or previous agricultural land, can release H₂S gas during excavation.Safety Measures for prevention of accidents:1.Training and Awareness: Proper training on the risks of H₂S and how to detect it is crucial. Workers should be educated on the signs of Hydrogen Sulphide Gas (H2S) exposure, such as the characteristic rotten egg smell, though reliance on smell is dangerous due to olfactory fatigue.2. Gas Monitoring and Detection Equipment: Use of portable gas detectors to monitor H₂S levels in real-time, especially before and during entry into confined spaces.3.Ventilation: Ensuring adequate ventilation in confined spaces to prevent the accumulation of hazardous gases.4.Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use of appropriate PPE, including respiratory protection, when working in areas with potential H₂S exposure.5.Emergency Response Management: Establishing and practicing emergency response procedures for H₂S exposure incidents.
More detailsPublished - Mon, 17 Jun 2024
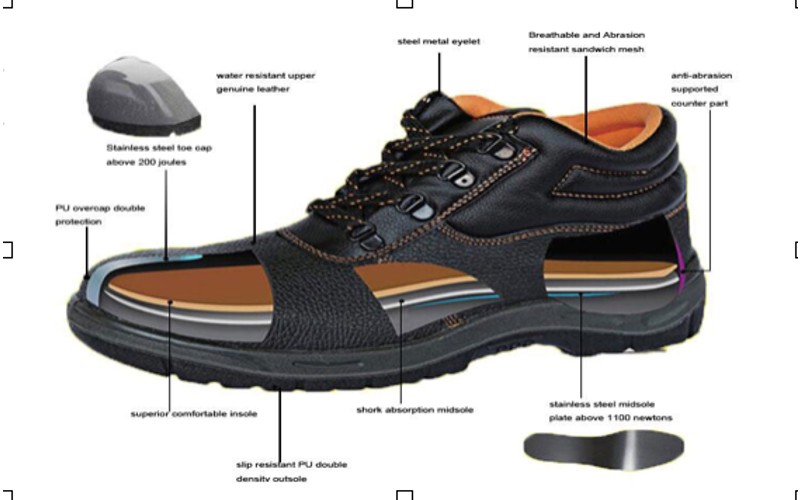

Created by - Elite Offshore
Industrial Safety Shoes: A crucial component of a Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Kit
In any industrial environment, safety should always be a top priority. One important aspect of workplace safety is proper footwear, which is a crucial part of any Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) required in an industrial environment. Industrial safety shoes are designed to protect workers' feet from a variety of hazards that are common in many industries, such as construction, manufacturing, and warehousing. These shoes ensure that workers can perform their tasks safely and efficiently.Industrial safety shoes are crafted to provide maximum protection while maintaining comfort for long hours of use. Here’s a brief overview of how they are made:1.Materials: Safety shoes are typically made from durable materials like leather, rubber, and synthetic fabrics. The upper part of the shoe is often made from tough leather to withstand wear and tear, while the soles are made from slip-resistant rubber.2.Toe Cap: One of the key components of safety shoes is the toe cap, which is usually made from steel, aluminum, or composite materials. This cap is designed to protect the toes from heavy falling objects or compression.3.Midsole: Many safety shoes include a midsole made from steel or other sturdy materials to protect against punctures from sharp objects like nails or glass.4.Design and Comfort: Modern safety shoes are designed with ergonomics in mind. They often include cushioned insoles, breathable linings, and padded collars to enhance comfort and reduce fatigue.Advantages of Industrial Safety Shoes1.Protection from Injuries: Safety shoes provide critical protection against a variety of injuries. The steel or composite toe caps protect against impacts, while puncture-resistant midsoles guard against sharp objects.2.Improved Traction: The slip-resistant soles of safety shoes help prevent slips and falls, which are common causes of workplace injuries. This is particularly important in environments where floors may be wet or oily.3.Comfort and Support: Good safety shoes are designed to provide support and comfort, which is essential for workers who spend long hours on their feet. Proper support can help prevent foot and lower limb fatigue and injuries.4.Durability: Made from high-quality materials, industrial safety shoes are built to last, providing long-term protection and value for money.Disadvantages of Industrial Safety Shoes1.Weight: One of the main drawbacks of safety shoes, particularly those with steel toe caps, is their weight. Heavier shoes can be tiring to wear for extended periods, although composite toe caps can be a lighter alternative.2.Breathability: Some safety shoes, especially those made from leather and with thick soles, may not be as breathable as regular footwear. This can lead to sweaty and uncomfortable feet, particularly in hot environments.Using industrial safety shoes in the workplace is essential for protecting workers from a range of potential hazards. While there are some disadvantages, the benefits far outweigh these concerns. Safety shoes offer critical protection, improve traction, and provide support, making them a necessary investment in ensuring workplace safety. For any further information, please contact training@eliteoffshore.in or call +91-22-4970 4933 or +91-80 9747 2277. You may visit our website Home (for all courses) or Ecademy The E-Learning Academy (for e-learning courses).Visit our training centre at below address:Elite Offshore Pvt. Ltd.G- 5, Platform Level, Tower-3, Belapur Railway Station Complex, Sector-11, C.B.D. Belapur, Navi Mumbai-400614.Contact No. +91-80-9747-2277, +91-22-4970-4933, +91-22-4600-3839Email: info@eliteoffshore.in or training@eliteoffshore.in
More detailsPublished - Mon, 17 Jun 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Role of Safety Signs in Promoting a Safer Work Environment
Safety signs play an important role in maintaining a safe and organized work environment. They communicate potential hazards and risks to employees and visitors and alert individuals to dangers such as slippery floors, electrical hazards, chemical exposures, or restricted areas. They serve as constant reminders about safe practices and procedures. Safety signs provide clear instructions on what actions to take to maintain safety. For example, they may indicate the location of emergency exits, first aid kits, fire extinguishers, or safety equipment. They contribute to creating a safer environment for everyone.During any emergencies, safety signs provide critical information quickly. They guide individuals to safety exits and emergency equipment, ensuring a prompt and organized response to crises like fires, chemical spills, or medical emergencies. In diverse workplaces, safety signs use universally recognized symbols and icons to overcome language barriers. This ensures that safety information is understood by all employees, regardless of their native language.Safety signs may be categorised as below:1. Warning signs 2. Prohibition signs 3. Emergency signs4. Hazard signs5. Road safety signs 6. Fire Safety Signs7. Construction safety signs8. Safety awareness signs9. Commercial floor signs10. Braille signsThus Safety signs play a crucial role and are integral to promoting a safety-conscious culture, preventing accidents, complying with regulations, and ensuring everyone in the workplace understands and follows essential safety protocols. These topics are adequately covered during various safety training programs e.g. Workplace Safety.
More detailsPublished - Thu, 18 Jul 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Career Progression and Opportunities in the Rigging Profession
The career of a RIGGER is both challenging and rewarding, requiring a combination of physical skill, technical knowledge, and a strong understanding of safety protocols. Rigging involves the safe handling, movement, and securing of heavy loads using various types of equipment such as cranes, hoists, and slings. The progression in this field typically follows a path from Rigger Level 1 to Rigger Level 4, with each stage involving increasingly complex tasks and responsibilities.Rigger Level 1: Starting the JourneyA Rigger Level 1 is often an entry-level position where individuals learn the basics of rigging. This stage focuses on simple, repetitive tasks, such as attaching rigging equipment, selecting appropriate rigging methods, and ensuring that all rigging setups are secure. At this level, the rigger works under supervision and deals with known load weights and configurations. The primary skills developed include inspecting rigging before use, identifying and selecting rigging components, and recognizing potential hazards in the rigging process. This stage is critical for building a solid foundation in rigging practices and safety standards.Rigger Level 4: Advancing in the FieldAs a rigger gains experience and confidence, they can progress to Rigger Level 4. This level allows for more independence and involves more complex rigging tasks, such as calculating load weights, determining the center of gravity, and selecting appropriate rigging components for specific jobs. A Rigger Level 4 can perform these tasks without supervision and is expected to have a deep understanding of load dynamics, hoisting equipment, and the various factors that can affect the stability and safety of a lift. This level of certification also includes performing pre-use inspections of rigging equipment and identifying lift points, which are crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operations.Career Opportunities and ProgressionRiggers have opportunities across various industries, including construction, oil and gas, manufacturing, shipping, and even the entertainment industry. The skills developed as a rigger are highly transferable, allowing individuals to move between different sectors. For example, construction riggers may transition into crane operation or specialize in specific rigging tasks like heavy lifting in offshore oil rigs.The progression from Rigger Level 1 to Level 4 not only increases job responsibilities but also opens up avenues for higher wages and specialized roles. Certification, often provided by recognized bodies like the API and National Commission for the Certification of Crane Operators (NCCCO), is crucial in advancing a rigger's career, as it demonstrates competence and adherence to safety standards. With experience and further training, riggers can advance to supervisory roles or specialize in more technical areas of rigging, such as crane operation or lift planning.In summary, a career as a rigger offers a structured path of progression with opportunities for specialization and advancement in various industries. The key to success in this field is continuous learning, hands-on experience, and a commitment to safety and precision in every task. For more detailed information on becoming a certified rigger and the specific tasks involved at each certification level, you can explore resources like the [NCCCO](https://www.nccco.org/) and specialized training providers like [Elite Offshore](https://eliteoffshore.in).
More detailsPublished - Sat, 31 Aug 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Enhancing Safety, Health, and Environmental Protection through Training
Human factors play a vital role in the safety, health, and environmental (HSE) performance of any organization. These factors refer to how people interact with their work environment, tasks, equipment, and procedures, and how these interactions influence overall safety and health. In high-risk industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing, construction, and maritime, paying attention to human factors through effective training can greatly improve HSE performance.A major area where human factors impact HSE is safety. Many workplace accidents occur due to human errors like poor judgment, lack of attention, or bad decisions. These mistakes are often preventable with proper training. Training programs that focus on identifying hazards, understanding safety procedures, and using equipment correctly help employees become more aware of risks. When workers are trained to recognize dangers and respond safely in critical situations, the chances of accidents and injuries drop significantly.Behavior-Based Safety (BBS) training is a powerful method to improve safety at work. It encourages safe behaviors and discourages risky actions by helping employees become aware of their unsafe habits. Through BBS training, workers can make positive changes in their behavior, which leads to fewer accidents and creates a strong safety-first culture within the organization. As a result, the overall health and safety standards of the workplace improve.Health is another important factor in HSE performance. In many industries, workers face health risks from exposure to hazardous materials, heavy machinery, or extreme working conditions. Training that focuses on health awareness can help employees protect themselves. For example, they can learn how to use personal protective equipment (PPE) properly, follow ergonomic practices to avoid injury, and understand the importance of regular health check-ups. A workforce that is healthy is more productive and less likely to experience workplace injuries or long-term illnesses.Environmental protection is also closely tied to human factors. Many industries have a direct impact on the environment, and employee behavior can make a big difference in how well an organization manages its environmental responsibilities. Training workers to follow environmental protection guidelines, such as proper waste management, pollution control, and resource conservation, can reduce harmful practices. When employees are aware of the environmental impact of their actions, they are more likely to make decisions that support sustainability, helping to reduce the company’s environmental footprint.Training is key to addressing human factors in HSE performance. It not only gives workers the knowledge and skills they need but also helps create a safety-first mindset throughout the organization. The best training programs combine both theory and hands-on exercises. For example, drills that simulate real-life situations like emergency evacuations, firefighting, and chemical spill responses allow employees to practice their skills in a controlled environment. This boosts their confidence and ensures they are prepared to act correctly in actual emergencies.Another benefit of focusing on human factors in HSE through training is improved teamwork and communication. In high-risk workplaces, good communication and teamwork are essential for preventing accidents. Training that emphasizes leadership, cooperation, and clear communication helps everyone work together toward shared safety and environmental goals.In conclusion, human factors are critical to improving HSE performance. By addressing safety, health, and environmental protection through targeted training, organizations can reduce accidents, improve worker well-being, and contribute to a safer, more sustainable environment.
More detailsPublished - Fri, 27 Sep 2024
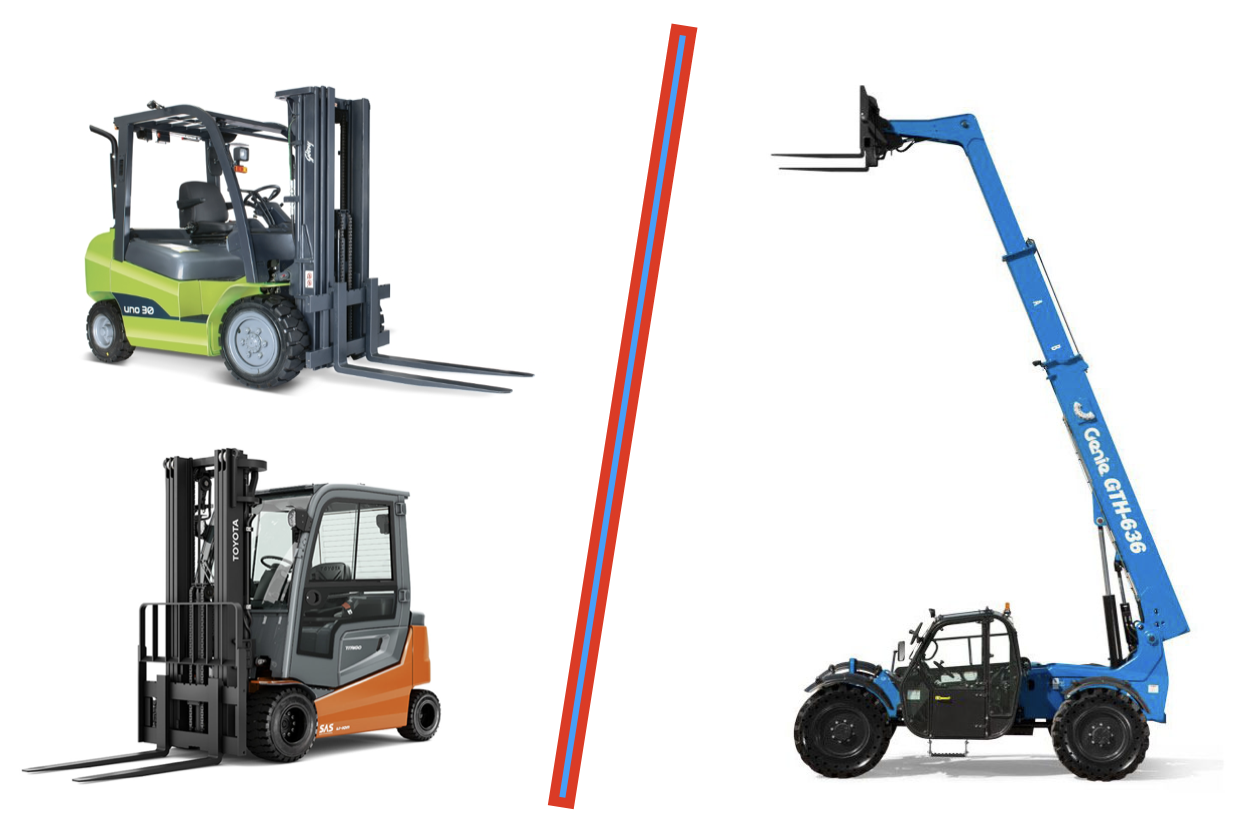

Created by - Elite Offshore
Telescopic Handlers (Telehandlers) vs Rough Terrain Forklifts
Telescopic handlers (telehandlers) and Rough terrain forklifts are both designed for heavy lifting in outdoor environments, but they serve slightly different purposes and have key structural differences. A comparison given below: A Telescopic Handler (Telehandler) A Rough Terrain Forklift1. Design and StructureA telehandler has an extendable telescoping boom that can reach both horizontally and vertically, much like a crane. This makes it more versatile for accessing elevated or hard-to-reach places. At the end of the boom, various attachments can be fitted, such as pallet forks, buckets, or work platforms.A Rough Terrain Forklift has a traditional mast and forks like standard forklifts but is equipped with large tires, heavy-duty suspension, and a reinforced frame to handle rough outdoor surfaces. It lifts vertically with a standard fork but lacks the telescoping boom.2. Lifting and Reach CapabilityThe extendable boom of telehandler allows it to lift loads to significant heights and reach forward across obstacles, making it useful for construction sites where materials need to be placed in elevated or otherwise inaccessible locations.The Rough Terrain Forklift can lift heavy loads and operate on uneven terrain, its reach is limited to vertical lifting. It cannot extend horizontally, so it’s typically used where loads need to be lifted and moved over shorter distances without height requirements.3. Versatility and AttachmentsTelehandlers are extremely versatile due to its range of compatible attachments, such as grapples, buckets, or winches, making it adaptable for various jobs.Rough Terrain Forklifts are primarily used for lifting and transporting palletized materials on rough ground. It’s generally limited to forks, though some models offer limited attachment options.4. Stability and ManeuverabilityTelehandlers are designed for stability, especially when using extended reaches. It often has outriggers or stabilizers to maintain balance when lifting heavy loads at high angles.Rough Terrain Forklifts typically are more compact and easier to maneuver in tighter spaces. Its heavy-duty tires and suspension are specifically designed for handling uneven ground without additional stabilizers, making it ideal for construction sites with limited space.5. Typical UsesTelehandlers are preferred for construction sites where materials need to be placed at height or moved across obstacles. It’s also popular in agriculture for stacking hay bales or loading materials.Rough Terrain Forklifts are commonly used in outdoor material handling and warehousing, especially in settings like lumber yards, stone yards, or agricultural sites where ground conditions are rough but loads don’t need to be lifted high or across obstacles.Thus while both are built for tough terrain, a telehandler is better for versatile lifting and reaching tasks, whereas a rough terrain forklift is ideal for lifting loads vertically and transporting them over uneven ground in tighter spaces.
More detailsPublished - Thu, 31 Oct 2024
Search
Popular categories
OSHA & Industrial Safety Courses
12Liberia Approved Rig Courses
4Marine and Offshore
3IADC Approved - E learning
2Offshore Oil and Gas Rig Courses
2Port & Marine Courses
1Latest blogs

What is a Face Fit Test & Why Is It Mandatory in Offshore Industry?
Thu, 12 Feb 2026

BOSIET & CA-EBS Safety Training Navi Mumbai | Elite Offshore Pvt Ltd
Tue, 10 Feb 2026

IADC RigPass vs BOSIET – what’s the difference?
Wed, 04 Feb 2026
Write a public review