
Created by - Elite Offshore
Enhancing Expertise: The Liberia Approved Maintenance Supervisor/Chief Mechanic Course at Elite Offshore
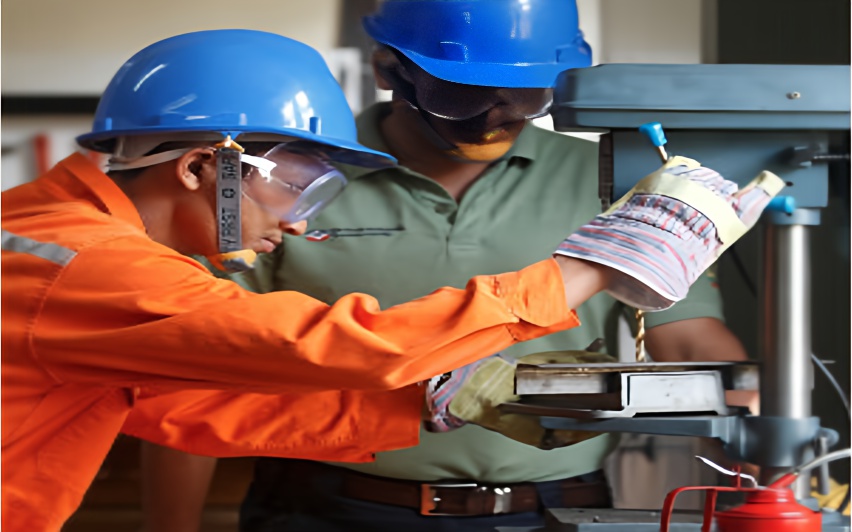
Elite Offshore conducts comprehensive training program on the Liberia flag (LISCR) approved Maintenance Supervisor / Chief Mechanic Course. Maintenance Supervisor course is as per IMO Resolution A.1079(28) adopted on 4th Dec 2013. This course is applicable for non propulsion vessel such as Construction, Pipe-lay and Accommodation barges; Semisub and Jackup drilling units etc which use anchor to stay in position. Tailored to meet the evolving demands of the offshore industry, this course equips participants with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in their roles as maintenance supervisors and chief mechanics. Elite Offshore's (https://eliteoffshore.in) commitment to excellence extends beyond its operational endeavors; it extends to nurturing talent and fostering professional growth within the industry. Designed by industry experts and approved by Liberia, a leading maritime authority, this course promises to elevate participants' capabilities to new heights. Course Contents: 1. Fundamentals of Maintenance Supervision: - Understanding the role and responsibilities of a maintenance supervisor. - Effective communication and leadership skills. - Resource allocation and scheduling techniques. 2. Mechanical Systems Overview: - In-depth exploration of mechanical systems commonly found in offshore environments. - Principles of operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting for engines, pumps, compressors, and more. - Safety considerations and best practices when working with mechanical equipment. 3. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: - Comprehensive study of hydraulic and pneumatic systems and their components. - Hands-on training in system design, maintenance, and repair. - Practical exercises to reinforce learning and develop proficiency. 4. Electrical Systems and Instrumentation: - Basics of electrical systems and instrumentation in offshore facilities. - Diagnosis and troubleshooting of electrical faults. - Safety protocols for working with electrical equipment in hazardous environments. 5. Preventive Maintenance Strategies: - Importance of preventive maintenance in ensuring equipment reliability and longevity. - Development and implementation of preventive maintenance plans. - Use of advanced tools and technologies for condition monitoring and predictive maintenance. 6. Emergency Response and Safety Procedures: - Preparation for emergency situations, including fire, gas leaks, and equipment failures. - Role-specific responsibilities during emergencies. - Simulation exercises and drills to simulate real-world scenarios and enhance response capabilities. 7. Regulatory Compliance and Documentation: - Familiarization with relevant regulations and standards governing offshore maintenance operations. - Documentation requirements for maintenance activities, inspections, and audits. - Importance of compliance in ensuring safety, environmental protection, and regulatory adherence. 8. Soft Skills Development: - Effective communication and interpersonal skills. - Conflict resolution and problem-solving techniques. - Time management and organizational skills. Advantages of the Course: 1. Industry-Relevant Curriculum: The course content is carefully crafted to address the specific challenges and requirements of maintenance supervision and chief mechanic roles in the offshore industry, crafted as per IMO Resolution A.1079(28) adopted on 4th Dec 2013. 2. Practical Learning Experience: Participants benefit from hands-on training sessions and simulation exercises, allowing them to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. 3. Professional Certification: Upon successful completion of the course, participants receive a Liberia-approved certification, validating their expertise and enhancing their career prospects. 4. Career Advancement Opportunities: The acquired skills and certification open doors to career advancement opportunities, including promotions to higher positions and greater responsibilities. 5. Enhanced Safety Awareness: Comprehensive training in emergency response and safety procedures equips participants with the skills and confidence to respond effectively to challenging situations, ensuring the safety of themselves and their colleagues. For any further information, please contact training@eliteoffshore.in or call +91-22-4970 4933 or +91-80 9747 2277. You may visit our website https://eliteoffshore.in (for all courses) or https://ecademy.eliteoffshore.in (for e-learning courses). Visit our training centre at below address: Elite Offshore Pvt. Ltd. G- 5, Platform Level, Tower-3, Belapur Railway Station Complex, Sector-11, C.B.D. Belapur, Navi Mumbai-400614. Contact No. +91-80-9747-2277, +91-22-4970-4933, +91-22-4600-3839 Email: info@eliteoffshore.in or training@eliteoffshore.in
More detailsPublished - Wed, 12 Jun 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Authorized Gas Tester (AGT) Training and Certification by Elite Offshore: Ensuring Safety in Industrial Environments
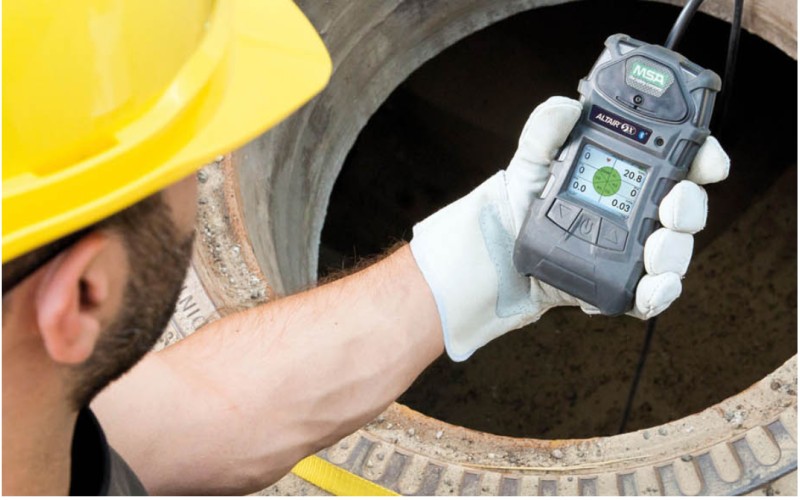
In industrial environments, particularly within the oil and gas sector, the presence of hazardous gases poses a significant risk to the safety of personnel. The need for skilled professionals who can accurately detect and manage these risks cannot be overstated. One such role is that of the Authorized Gas Tester (AGT); whose primary responsibility is to ensure the safety of workers during confined space entry and other potentially hazardous operations. Elite Offshore, a premier provider of safety and technical training, offers a comprehensive AGT training and certification program designed to equip individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform this critical role effectively.The Importance of AGT in Industrial EnvironmentsConfined spaces in industrial settings often contain dangerous levels of toxic or flammable gases. These gases can lead to fatal accidents if not properly managed. An AGT plays a crucial role in preventing such incidents by:1.Ensuring Safe Work Conditions: Before any operation in a confined space begins, an AGT tests the atmosphere to confirm it is safe for entry. This helps prevent exposure to harmful gases that could lead to asphyxiation, poisoning, or explosions.2.Monitoring Ongoing Safety: During operations, the AGT continuously monitors gas levels to detect any changes that could pose a risk. This ongoing vigilance is essential for maintaining a safe working environment.3.Compliance with Regulations: The AGT ensures that all gas testing and monitoring activities comply with industry regulations and safety standards, thereby avoiding legal and financial repercussions for the organization.Roles and Responsibilities of an Authorized Gas Tester (AGT)The role of an AGT comprises of a wide range of responsibilities, all aimed at ensuring safety in hazardous environments. These responsibilities include:1. Conducting Pre-Entry Gas TestingBefore workers enter a confined space, the AGT conducts thorough gas testing to detect the presence of any hazardous gases. This involves using specialized equipment to measure gas concentrations and ensure they are within safe limits.2. Continuous MonitoringThe AGT is responsible for continuously monitoring the atmosphere during operations. This includes periodic re-testing to detect any changes in gas levels that could compromise safety.3. Equipment Calibration and MaintenanceThe AGT must ensure that all gas detection equipment is properly calibrated and maintained. This involves regular checks and servicing to ensure accurate readings.4. Implementing Safety ProtocolsThe AGT implements and enforces safety protocols, such as issuing permits to work, conducting risk assessments, and ensuring that all safety measures are in place before operations commence.5. Emergency ResponseIn the event of a gas-related emergency, the AGT is responsible for initiating emergency response procedures, including evacuation and first aid. They must be prepared to act swiftly and decisively to protect the safety of all personnel.6. Training and AdvisingAGTs often take on a training role, educating other workers about the dangers of hazardous gases and the importance of gas testing. They also provide advice on best practices for working safely in confined spaces.Authority of the AGTThe AGT holds significant authority in industrial settings, particularly regarding safety decisions. They have the power to:- Halt operations if unsafe gas levels are detected.- Deny entry to confined spaces until safety conditions are met.- Enforce compliance with safety protocols and regulations.- Issue permits for confined space entry and other hazardous operations.This authority underscores the critical nature of their role in maintaining workplace safety.Topics Covered in Elite Offshore's AGT TrainingElite Offshore's AGT training program is meticulously designed to cover all aspects necessary for the effective performance of an AGT. The program adheres to industry standards and includes the following key topics:1. Understanding the Roles and Responsibilities of an AGTThe training begins with an overview of the roles and responsibilities of an AGT. This section emphasizes the importance of their role in ensuring workplace safety and outlines the ethical and legal obligations they must uphold.2. Gas Detection and Monitoring EquipmentParticipants are introduced to various types of gas detection and monitoring equipment. The training covers the principles of gas detection technology, the use of portable and fixed gas detectors, and the maintenance and calibration of equipment.3. The Hazards and Properties of GasesThis module provides in-depth knowledge of common hazardous gases encountered in industrial settings. Participants learn about the physical and chemical properties of these gases, their health effects, and the conditions under which they become dangerous.4. Safe Systems of WorkParticipants are taught the importance of safe systems of work, including the implementation of permits to work, risk assessments, and emergency response plans. This module emphasizes the need for thorough planning and coordination to ensure safety.5. Confined Space Entry ProceduresConfined spaces pose unique hazards that require specialized knowledge. This module covers the procedures for safe entry into confined spaces, including the identification of confined spaces, risk assessment, and control measures.6. Interpreting Gas Test Results and DocumentationParticipants are trained to accurately interpret gas test results and document their findings. This includes understanding gas concentration levels, making informed decisions based on data, and maintaining accurate records for compliance purposes.Benefits of Elite Offshore’s AGT Training ProgramElite Offshore’s AGT training program offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice for individuals and organizations alike:Comprehensive CurriculumThe training program covers all essential topics, ensuring that participants gain a thorough understanding of their roles and responsibilities as AGTs. The curriculum is designed to meet industry standards and provide practical knowledge and skills.Flexible E-Learning PlatformMyntra Global's E-learning platform allows participants to access training materials at their convenience. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for offshore workers with irregular schedules or those who cannot attend traditional classroom training.Interactive and Engaging Learning ExperienceThe e-learning platform incorporates a variety of interactive elements, such as simulations, videos, and quizzes, to create an engaging learning experience. These interactive features enhance knowledge retention and provide practical, hands-on experience.Industry-Recognized CertificationUpon successful completion of the training program, participants receive certification by OPITO that is recognized throughout the industry. This certification demonstrates their competency as Authorized Gas Testers and their commitment to maintaining high safety standards.Cost-Effective Training SolutionThe e-learning format reduces the need for travel and accommodation expenses associated with traditional classroom training. Additionally, the scalability of e-learning allows organizations to train multiple employees simultaneously, reducing overall training costs.Thus the role of an Authorized Gas Tester is critical in ensuring the safety of industrial environments, particularly during confined space entry and operations. Elite Offshore’s AGT training and certification program provides a comprehensive and flexible training solution that equips individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform this vital role effectively. By covering essential topics such as gas detection and monitoring, the hazards and properties of gases, safe systems of work, and confined space entry procedures, the program ensures that participants are well-prepared to uphold safety standards in their workplaces. For any further information, please contact training@eliteoffshore.in or call +91-22-4970 4933 or +91-80 9747 2277. You may visit our website https://eliteoffshore.in (for all courses) or https://ecademy.eliteoffshore.in (for e-learning courses).Visit our training centre at below address:Elite Offshore Pvt. Ltd.G- 5, Platform Level, Tower-3, Belapur Railway Station Complex, Sector-11, C.B.D. Belapur, Navi Mumbai-400614.Contact No. +91-80-9747-2277, +91-22-4970-4933, +91-22-4600-3839Email: info@eliteoffshore.in or training@eliteoffshore.in
More detailsPublished - Mon, 17 Jun 2024
Created by - Elite Offshore
Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S): Accidents and Prevention in construction industry
Hydrogen Sulphide Gas (H2S) accidents are not as common in the construction industry as in other sectors like oil and gas or wastewater treatment. However, they do occur and can be extremely dangerous when they happen. Hydrogen sulfide is normally formed where organic matter is decomposing under anaerobic (oxygen-free) conditions. It is a toxic and flammable gas.Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S) Accidents in Construction industry may be present in:1.Confined Space Entry (CSE): H₂S accidents in the construction industry often occur in confined spaces such as sewers, manholes, and underground utility vaults. Workers entering these spaces without proper atmospheric testing and ventilation are at risk of exposure.2.Excavation, Trenching and Shoring Sites: Construction sites involving excavation near areas with known contamination or organic matter (e.g., near landfills or wastewater treatment facilities) can pose a risk of H₂S exposure.3.Decomposition of Organic Material: Construction activities in areas with high concentrations of organic materials, such as certain types of soil or previous agricultural land, can release H₂S gas during excavation.Safety Measures for prevention of accidents:1.Training and Awareness: Proper training on the risks of H₂S and how to detect it is crucial. Workers should be educated on the signs of Hydrogen Sulphide Gas (H2S) exposure, such as the characteristic rotten egg smell, though reliance on smell is dangerous due to olfactory fatigue.2. Gas Monitoring and Detection Equipment: Use of portable gas detectors to monitor H₂S levels in real-time, especially before and during entry into confined spaces.3.Ventilation: Ensuring adequate ventilation in confined spaces to prevent the accumulation of hazardous gases.4.Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use of appropriate PPE, including respiratory protection, when working in areas with potential H₂S exposure.5.Emergency Response Management: Establishing and practicing emergency response procedures for H₂S exposure incidents.
More detailsPublished - Mon, 17 Jun 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Liberia Flag Approved Offshore Installation Manager (OIM) Training by Elite Offshore
The offshore oil and gas industry is a high-stakes field requiring rigorous training and certification to ensure safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. One of the most crucial roles within this industry is that of the Offshore Installation Manager (OIM). The OIM is responsible for the overall management of offshore installations, encompassing everything from safety and operations to crew welfare and emergency response. Elite Offshore, a leading training provider, offers a comprehensive Liberia flag-approved OIM training program designed to meet the highest standards set by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and other regulatory bodies.Importance of OIM TrainingThe role of an OIM is multifaceted and demanding. Effective training is critical to ensure that OIMs possess the necessary skills and knowledge to manage offshore installations safely and efficiently. The training program by Elite Offshore not only meets regulatory requirements but also provides participants with hands-on experience and real-world scenarios to enhance their learning.Duties and Responsibilities of an OIMThe Offshore Installation Manager holds a pivotal role in the offshore industry. Their duties and responsibilities are diverse, encompassing several critical areas:Safety Management1. Ensuring Safety Compliance: The OIM is responsible for ensuring that all operations comply with safety regulations and standards. This includes regular safety drills, inspections, and adherence to safety protocols.2. Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Conducting risk assessments and implementing measures to mitigate identified risks. The OIM must be proactive in identifying potential hazards and taking steps to prevent accidents.3. Emergency Response Coordination: In the event of an emergency, the OIM coordinates the response, ensuring that all personnel are aware of their roles and responsibilities. This includes managing evacuation procedures and liaising with rescue services.Operational Management1. Overseeing Operations: The OIM oversees all operations on the installation, ensuring that they are carried out efficiently and safely. This includes drilling, production, and maintenance activities.2. Resource Management: Managing resources, including personnel, equipment, and supplies, to ensure that operations run smoothly. The OIM must balance the needs of different departments and prioritize tasks effectively.3. Maintenance Oversight: Ensuring that all equipment and systems are properly maintained and operational. This includes scheduling regular maintenance and addressing any issues promptly to prevent downtime.Personnel Management1. Supervising Crew: The OIM supervises the crew, ensuring that they are well-trained, motivated, and working safely. This includes conducting performance reviews, providing feedback, and addressing any issues that arise.2. Training and Development: Overseeing the training and development of personnel, ensuring that they have the skills and knowledge required to perform their duties effectively.3. Welfare and Morale: Ensuring the welfare and morale of the crew, addressing any concerns, and fostering a positive working environment. This includes managing accommodations, catering, and recreational facilities.Regulatory Compliance1. Adhering to Regulations: Ensuring that the installation complies with all relevant regulations and standards. This includes environmental regulations, health and safety standards, and industry best practices.2. Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of all operations, incidents, and maintenance activities. These records are essential for regulatory compliance and for identifying areas for improvement.3. Audit and Inspection: Preparing for and managing audits and inspections by regulatory bodies. The OIM must ensure that all documentation is up-to-date and that the installation is ready for inspection at all times.Communication and Reporting1. Liaising with Stakeholders: Communicating with stakeholders, including the installation owner, regulatory bodies, and other relevant parties. The OIM must provide regular updates on operations, safety, and any issues that arise.2. Incident Reporting: Reporting incidents, near misses, and any other significant events to the appropriate authorities. This includes conducting investigations and implementing corrective actions to prevent recurrence.3. Daily Reporting: Providing daily reports on operations, highlighting any issues or concerns, and outlining plans for the coming days.Liberia Flag-Approved OIM Training by Elite OffshoreThe Liberia flag-approved OIM training program offered by Elite Offshore is designed to meet the highest standards of the industry. The program covers all aspects of the OIM role, ensuring that participants are well-prepared to take on this critical position.Training Program ContentThe content of the training program is based on the guidelines set out in IMO Resolution A.1079(28), dated December 4, 2013. The resolution outlines the competencies required for OIMs, focusing on safety, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.Certification and AccreditationUpon successful completion of the Liberia flag-approved OIM training program, participants receive a certification that is recognized by the Liberia Maritime Authority. This certification demonstrates that they have met the highest standards of training and are qualified to take on the role of an OIM.The Offshore Installation Manager (OIM) plays a crucial role in the offshore oil and gas industry, overseeing operations, ensuring safety, and managing personnel. Effective training is essential to prepare OIMs for the demands of their role, ensuring that they have the skills and knowledge required to manage offshore installations safely and efficiently.
More detailsPublished - Mon, 17 Jun 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Industrial Safety Shoes: A crucial component of a Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Kit
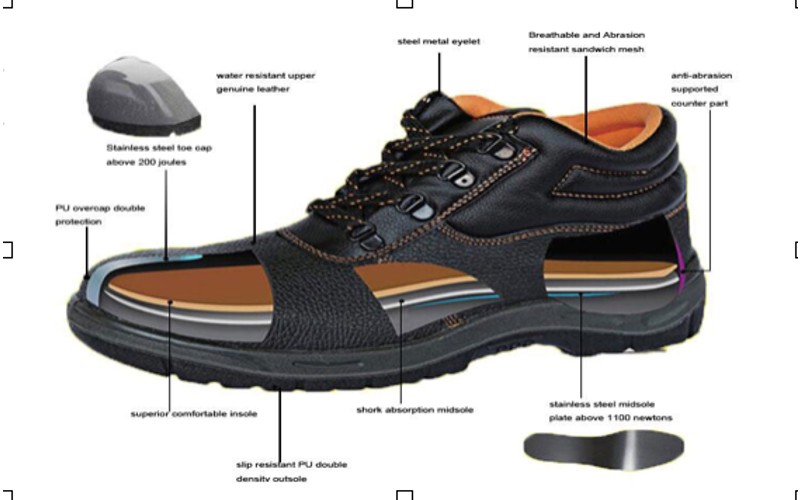
In any industrial environment, safety should always be a top priority. One important aspect of workplace safety is proper footwear, which is a crucial part of any Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) required in an industrial environment. Industrial safety shoes are designed to protect workers' feet from a variety of hazards that are common in many industries, such as construction, manufacturing, and warehousing. These shoes ensure that workers can perform their tasks safely and efficiently.Industrial safety shoes are crafted to provide maximum protection while maintaining comfort for long hours of use. Here’s a brief overview of how they are made:1.Materials: Safety shoes are typically made from durable materials like leather, rubber, and synthetic fabrics. The upper part of the shoe is often made from tough leather to withstand wear and tear, while the soles are made from slip-resistant rubber.2.Toe Cap: One of the key components of safety shoes is the toe cap, which is usually made from steel, aluminum, or composite materials. This cap is designed to protect the toes from heavy falling objects or compression.3.Midsole: Many safety shoes include a midsole made from steel or other sturdy materials to protect against punctures from sharp objects like nails or glass.4.Design and Comfort: Modern safety shoes are designed with ergonomics in mind. They often include cushioned insoles, breathable linings, and padded collars to enhance comfort and reduce fatigue.Advantages of Industrial Safety Shoes1.Protection from Injuries: Safety shoes provide critical protection against a variety of injuries. The steel or composite toe caps protect against impacts, while puncture-resistant midsoles guard against sharp objects.2.Improved Traction: The slip-resistant soles of safety shoes help prevent slips and falls, which are common causes of workplace injuries. This is particularly important in environments where floors may be wet or oily.3.Comfort and Support: Good safety shoes are designed to provide support and comfort, which is essential for workers who spend long hours on their feet. Proper support can help prevent foot and lower limb fatigue and injuries.4.Durability: Made from high-quality materials, industrial safety shoes are built to last, providing long-term protection and value for money.Disadvantages of Industrial Safety Shoes1.Weight: One of the main drawbacks of safety shoes, particularly those with steel toe caps, is their weight. Heavier shoes can be tiring to wear for extended periods, although composite toe caps can be a lighter alternative.2.Breathability: Some safety shoes, especially those made from leather and with thick soles, may not be as breathable as regular footwear. This can lead to sweaty and uncomfortable feet, particularly in hot environments.Using industrial safety shoes in the workplace is essential for protecting workers from a range of potential hazards. While there are some disadvantages, the benefits far outweigh these concerns. Safety shoes offer critical protection, improve traction, and provide support, making them a necessary investment in ensuring workplace safety. For any further information, please contact training@eliteoffshore.in or call +91-22-4970 4933 or +91-80 9747 2277. You may visit our website Home (for all courses) or Ecademy The E-Learning Academy (for e-learning courses).Visit our training centre at below address:Elite Offshore Pvt. Ltd.G- 5, Platform Level, Tower-3, Belapur Railway Station Complex, Sector-11, C.B.D. Belapur, Navi Mumbai-400614.Contact No. +91-80-9747-2277, +91-22-4970-4933, +91-22-4600-3839Email: info@eliteoffshore.in or training@eliteoffshore.in
More detailsPublished - Mon, 17 Jun 2024
Created by - Elite Offshore
Advantages of a Blended Product training Vs Traditional training methods
Blended product training combines the best elements of both online and face-to-face instruction, offering several distinct advantages over traditional training methods. Here’s a closer look at the benefits of this approach:1.Flexibility and ConvenienceOnline Components:Self-Paced Learning: Participants can complete online modules at their own pace, allowing them to balance training with their work schedules.Anytime, Anywhere Access: Learners can access training materials from any location and at any time, reducing the need for travel and time away from work. 2.Enhanced Engagement and RetentionVariety of Formats:Interactive Content: Blended training often includes videos, quizzes, interactive simulations, and gamified elements, which can make learning more engaging and enjoyable. -In-Person Interaction: Face-to-face sessions provide opportunities for hands-on practice, group discussions, and real-time feedback, enhancing understanding and retention. 3.Cost-EffectivenessReduced Costs:Travel and Accommodation: Shifting a portion of the training online reduces the need for travel and lodging expenses for both trainers and trainees.Scalable Resources: Online modules can be reused and scaled to accommodate large numbers of learners without significant additional costs. 4.Comprehensive Learning ExperienceIntegration of Theory and Practice:-Theoretical Foundation: Online modules can deliver foundational knowledge and theory efficiently, ensuring all learners start with a common understanding.-Practical Application: In-person sessions allow learners to apply what they've learned in real-world scenarios, reinforcing their skills and understanding. 5.Improved Tracking and AnalyticsLearning Management Systems (LMS): An LMS can track learner progress, completion rates, and performance on assessments, providing valuable data for continuous improvement.Analytics and Reporting: Detailed analytics help trainers and organizations identify areas where learners are struggling and adjust the training program accordingly. 6.Enhanced Assessment and FeedbackRegular Quizzes and Tests: Online modules can include regular quizzes and assessments to gauge understanding and retention.Immediate Feedback: Automated systems can provide immediate feedback on online assessments, while in-person sessions offer opportunities for direct, personalized feedback from trainers.Blended product training solutions offer numerous advantages over traditional training methods. By combining the flexibility and accessibility of online learning with the interactive and hands-on benefits of in-person sessions, blended training provides a comprehensive, engaging, and effective learning experience. This approach not only enhances learner engagement and retention but also offers significant cost savings, scalability, and the ability to deliver personalized, high-quality training consistently.
More detailsPublished - Wed, 19 Jun 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Importance of Magnetic Compass Adjustment Aboard Ships
Importance of Magnetic Compass Adjustment Aboard ShipsNavigating the vast and unpredictable oceans has been a hallmark of human exploration and commerce for centuries. From ancient seafarers guided by the stars to modern maritime professionals relying on sophisticated technology, one instrument has stood the test of time as a fundamental tool of navigation: the magnetic compass. Despite advancements in electronic navigation systems like GPS, the magnetic compass remains indispensable, serving as a reliable backup and essential tool for maintaining course and ensuring the safety of ships at sea.The Magnetic Compass as the Foundation of navigationThe magnetic compass is a simple yet ingenious device that aligns itself with the Earth's magnetic field, indicating the direction of magnetic north. This fundamental principle has guided sailors and explorers across oceans and continents, providing a constant reference point even in the absence of visible landmarks or celestial cues.On modern ships, the magnetic compass continues to play a crucial role alongside Gyro Compass which is an electronic navigation aid. Its importance lies not only in its simplicity and reliability but also in its regulatory requirement aboard all vessels, ensuring compliance with international maritime laws and safety standards.Understanding Magnetic Compass AdjustmentTo appreciate the significance of magnetic compass adjustment, it is essential to understand the factors that affect its accuracy. The Earth's magnetic field is not uniform, and onboard magnetic influences from the ship's structure and equipment can cause deviations, known as compass errors. These errors can lead to inaccuracies in directional readings, potentially jeopardizing safe navigation. The two main errors experienced are known as Deviation and Variation.Magnetic compass adjustment, also known as compass swinging or compass compensation, involves techniques to minimize these errors and ensure the compass provides accurate readings. This adjustment process is critical for several reasons:1. Safety and ReliabilityThe primary reason for magnetic compass adjustment is to enhance the safety and reliability of navigation at sea. Imagine a scenario where electronic navigation systems fail due to a technical glitch or a cyber-attack. In such situations, the magnetic compass becomes the primary means of determining the ship's heading. Ensuring its accuracy through regular adjustment is crucial for maintaining course and avoiding navigational hazards.2. Compliance with International RegulationsInternational maritime regulations, including those established by the International Maritime Organization (IMO), mandate that all vessels must have properly adjusted and calibrated magnetic compasses. These regulations are designed to ensure uniform standards of safety and operational competence across the global maritime industry.3. Reducing Compass Deviation and VariationCompass deviation refers to the discrepancies between the magnetic compass readings and the actual direction of true north. This deviation can be caused by various factors, such as the presence of ferrous metals, electrical equipment, and magnetic anomalies aboard the ship. Without proper adjustment, these deviations can lead to navigational errors, potentially resulting in course deviations, collisions, or groundings.Through meticulous adjustment techniques, compass adjusters mitigate these deviations by compensating for onboard magnetic influences. This process involves carefully measuring and calculating the effects of deviation on the compass readings and applying corrections to ensure accuracy.The Variation is the difference between the magnetic north your compass points to and true north. – This difference is caused by the Earth's magnetic field. This error is fixed for a particular location on earth and varies with time. This error is mentioned on the chart and need so be applied while making compass adjustments.4. Enhancing Navigation EfficiencyIn today's maritime industry, where efficiency and precision are paramount, accurately adjusted magnetic compasses contribute to efficient navigation operations. They provide reliable directional information that complements electronic navigation systems, offering redundancy in case of system failures or emergencies.Moreover, for vessels navigating in regions with limited GPS coverage or where electronic navigation aids are unreliable, a well-adjusted magnetic compass remains an invaluable asset. It serves as a dependable backup, ensuring continuous navigation capability regardless of external conditions.5. Professional Competence and Skill DevelopmentFor maritime professionals, proficiency in magnetic compass adjustment is important and crucial. It demonstrates a thorough understanding of navigational principles and the ability to apply them effectively in real-world scenarios.Courses and training programs, such as those offered by institutions like Elite Offshore, play a pivotal role in equipping compass adjusters with the knowledge and practical skills needed to perform their duties competently. These programs cover a wide range of topics, including the theory of magnetism, adjustment techniques, regulatory requirements, and practical hands-on sessions using specialized equipment.The importance of magnetic compass adjustment aboard ships cannot be overstated. It serves as a foundational element of maritime navigation, ensuring the safety, compliance, and efficiency of vessels navigating the world's oceans. Through rigorous training, adherence to international regulations, and meticulous adjustment techniques, maritime professionals uphold the standards of navigational excellence that have defined the industry for centuries.
More detailsPublished - Mon, 08 Jul 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Role of Safety Signs in Promoting a Safer Work Environment
Safety signs play an important role in maintaining a safe and organized work environment. They communicate potential hazards and risks to employees and visitors and alert individuals to dangers such as slippery floors, electrical hazards, chemical exposures, or restricted areas. They serve as constant reminders about safe practices and procedures. Safety signs provide clear instructions on what actions to take to maintain safety. For example, they may indicate the location of emergency exits, first aid kits, fire extinguishers, or safety equipment. They contribute to creating a safer environment for everyone.During any emergencies, safety signs provide critical information quickly. They guide individuals to safety exits and emergency equipment, ensuring a prompt and organized response to crises like fires, chemical spills, or medical emergencies. In diverse workplaces, safety signs use universally recognized symbols and icons to overcome language barriers. This ensures that safety information is understood by all employees, regardless of their native language.Safety signs may be categorised as below:1. Warning signs 2. Prohibition signs 3. Emergency signs4. Hazard signs5. Road safety signs 6. Fire Safety Signs7. Construction safety signs8. Safety awareness signs9. Commercial floor signs10. Braille signsThus Safety signs play a crucial role and are integral to promoting a safety-conscious culture, preventing accidents, complying with regulations, and ensuring everyone in the workplace understands and follows essential safety protocols. These topics are adequately covered during various safety training programs e.g. Workplace Safety.
More detailsPublished - Thu, 18 Jul 2024

Created by - Elite Offshore
Career Progression and Opportunities in the Rigging Profession
The career of a RIGGER is both challenging and rewarding, requiring a combination of physical skill, technical knowledge, and a strong understanding of safety protocols. Rigging involves the safe handling, movement, and securing of heavy loads using various types of equipment such as cranes, hoists, and slings. The progression in this field typically follows a path from Rigger Level 1 to Rigger Level 4, with each stage involving increasingly complex tasks and responsibilities.Rigger Level 1: Starting the JourneyA Rigger Level 1 is often an entry-level position where individuals learn the basics of rigging. This stage focuses on simple, repetitive tasks, such as attaching rigging equipment, selecting appropriate rigging methods, and ensuring that all rigging setups are secure. At this level, the rigger works under supervision and deals with known load weights and configurations. The primary skills developed include inspecting rigging before use, identifying and selecting rigging components, and recognizing potential hazards in the rigging process. This stage is critical for building a solid foundation in rigging practices and safety standards.Rigger Level 4: Advancing in the FieldAs a rigger gains experience and confidence, they can progress to Rigger Level 4. This level allows for more independence and involves more complex rigging tasks, such as calculating load weights, determining the center of gravity, and selecting appropriate rigging components for specific jobs. A Rigger Level 4 can perform these tasks without supervision and is expected to have a deep understanding of load dynamics, hoisting equipment, and the various factors that can affect the stability and safety of a lift. This level of certification also includes performing pre-use inspections of rigging equipment and identifying lift points, which are crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operations.Career Opportunities and ProgressionRiggers have opportunities across various industries, including construction, oil and gas, manufacturing, shipping, and even the entertainment industry. The skills developed as a rigger are highly transferable, allowing individuals to move between different sectors. For example, construction riggers may transition into crane operation or specialize in specific rigging tasks like heavy lifting in offshore oil rigs.The progression from Rigger Level 1 to Level 4 not only increases job responsibilities but also opens up avenues for higher wages and specialized roles. Certification, often provided by recognized bodies like the API and National Commission for the Certification of Crane Operators (NCCCO), is crucial in advancing a rigger's career, as it demonstrates competence and adherence to safety standards. With experience and further training, riggers can advance to supervisory roles or specialize in more technical areas of rigging, such as crane operation or lift planning.In summary, a career as a rigger offers a structured path of progression with opportunities for specialization and advancement in various industries. The key to success in this field is continuous learning, hands-on experience, and a commitment to safety and precision in every task. For more detailed information on becoming a certified rigger and the specific tasks involved at each certification level, you can explore resources like the [NCCCO](https://www.nccco.org/) and specialized training providers like [Elite Offshore](https://eliteoffshore.in).
More detailsPublished - Sat, 31 Aug 2024
Search
Popular categories
OSHA & Industrial Safety Courses
12Liberia Approved Rig Courses
4Marine and Offshore
3IADC Approved - E learning
2Offshore Oil and Gas Rig Courses
2Port & Marine Courses
1Latest blogs

What is a Face Fit Test & Why Is It Mandatory in Offshore Industry?
Thu, 12 Feb 2026

BOSIET & CA-EBS Safety Training Navi Mumbai | Elite Offshore Pvt Ltd
Tue, 10 Feb 2026

IADC RigPass vs BOSIET – what’s the difference?
Wed, 04 Feb 2026
Write a public review